Types of market failure
The meaning of externalities
Externality: is an unintended side effect that result from production or consumption of a good, affecting the third parties.
- When this is externality, the market does not achieve a social optimum where MSB=MSC
- Negative externalities → also called spill-over costs or social costs
- Positive externalities → also called spill-over benefits or social benefits
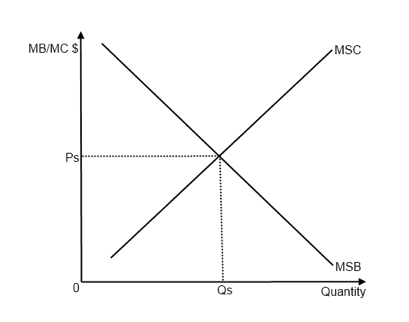
Social equilibrium: occurs at Ps, Qs
Internalizing an externality: is a government action to achieve socially desirable equilibrium for the economy.
Negative externalities of production and consumption
Negative externalities of production: is a harmful side effect to the society due to the production by a firm.
i.e. Factory releasing poisoning materials that are harmful to the area; Power house burning fossil fuels, releasing greenhouse gases that would cause global warming.

- There is a misallocation of resources: too much is being produced at a too low price than is socially desirable.
- There is a welfare lost to society of the extra units from Qp to Qs because MSC is greater than MSB (shaded area)
Negative externalities of consumption: is a harmful side effect to the society due to the consumption by an individual.
i.e. Smokers giving passive smoking to other people, causing them to get illnesses.
Figure 4.3 - A negative externality of consumption
- This is a misallocation of resources: too much is being consumed at a too high price than is socially desirable.
- There is welfare lost to society of the extra units from Qp to Qs because MSC is greater than MSB (shaded area)
Demerit goods: are goods that the government thinks are bad both for the consumer and the society. They are over-provided by the market and will be over-consumed.
- They are examples for negative externalities of consumption
Internalizing a negative externality:
- Market based policies: Taxation & tradable permits → increase private costs to firms → MPC shifts up towards the point of socially desirable equilibrium
- Government regulations: Banning → stops the consumption or production completely; Restricting outputs → increase private costs for firms to meet the standard → MPC shifts up towards the point of socially desirable equilibrium
- Publicity campaign → provide education on demerit goods OR fund negative advertising on demerit goods → less consumption → shifts MPB to left towards the point of socially desirable equilibrium
