Supply
The law of supply
Supply: is the total amount of goods and services that producers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period.
The law of supply: states that "as the price of a product rises, the quantity supplied of the product will usually increase, ceteris paribus".
- price rises but costs do not change → profitability increases → supply more (increase profits)
The supply curve
Supply curve: represents the relationship between the price and the quantity supplied of a product, ceteris paribus.
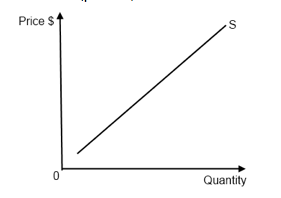
Figure 1.3 - The supply curve
The non-price determinants of supply (factors that change supply or shift the supply curve)
The non-price determinants of supply (shifting):
- Changes in costs of factors of production: Increase in costs of production → supply shifts to the left
- land
- labor
- capital
- entrepreneurship (human capital or intellectual capital)
- State of technology: Improvements in technology → supply shifts to the right (natural disasters may move the technology backwards → supply shifts to the left)
- Price of relating product (joint/competitive supply): if producer could produce another product with higher profit, due to limited resources, the supply for the existing product decreases.
- Expectations: if demand for the product is likely to rise → supply increases (ready to supply more in the future and gain higher profit)
- Indirect taxes & subsidies:
- Indirect taxes → increase costs → supply shifts left
- Subsidies → reduce costs → supply shifts right
- Number of firms in the market: more firms producing → supply shifts to the right → more are being supplied at each price level
Movements along and shifts of the supply curve
Movements along the supply curve:
- A change in price of the good itself leads to a movement along the existing supply curve (price is the axes), while a change in any other determinants of supply will always lead to a shift of the demand curve to either left or to the right.
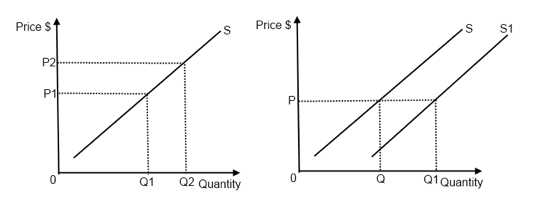
Figure 1.4 - Movement along and shift of the supply curve
Linear supply functions, equations and graphs
Linear Supply functions:
Where:
- c = quantity supplied when price is zero
- d = slope of the curve
|
Price $ |
Calculation |
Quantity supplied |
|
0 |
|
(-30)→ 0 |
|
1 |
|
(-10)→ 0 |
|
2 |
|
10 |
|
3 |
|
30 |
If:
- c changes → shift of supply curve
- d changes → change of steepness of supply curve
